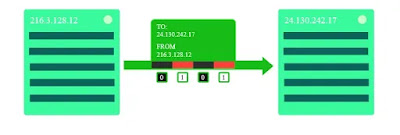
The Internet Protocol (IP) describes, but a pair of computers can communicate with each other, and it's utilized by every portable computer on the online.
Each portable computer has associate science address, almost like homes and companies have mail addresses.
When a portable computer sends a message to a distinct portable computer, it specifies the recipient's address and in addition makes sure to embrace its own address, that the second portable computer can reply.
The IP address may be a fascinating product of recent engineering designed to permit one connected pc (or "smart" device) to speak with another device over the net.IP addresses enable the situation of virtually billions of digital devices that square measure connected to the net to be pinpointed and differentiated from alternative devices.
Because, within the same manner you to wish a address to recieve a letter within the mail from an addict, a far off pc wants your IP address to speak along with your pc.
The IP address you are using at any given time is your device's "digital address" that permits a affiliation to the consistently laid-out, interconnected grid that governs international property.But are you able to take care IP address is 100% reliable?
When anyone pops a letter in a very mail box, you do not trust its route, or what number trucks the communication workplace uses, or what number packages the mailman delivers each day. you only need it to travel the correct address.
Want to Know one thing additional cool?
Every web site (Disney, Amazon, Apple, Google, etc.) contains a distinctive IP address, however it goes by its name instead (Disney.com, Amazon.com, Apple.com, Google.com.) however while not IP addresses could no connect with them and that they couldn't share info with you.
The IPv4 Address
Internet Protocol version four, typically spoken as IPv4, was developed within the early Eighties. associate degree IPv4 address contains four numbers, every starting from zero to 255, that are separated by periods. for instance, Google IP address is 8.8.8.8. there's a lot of to IP addresses, and it helps to grasp the necessities of TCP/IP also, however these ar the fundamentals.
Every web site has associate degree IP address, we tend to simply don’t use them any longer, typically. within the youth of the net, it absolutely was necessary to grasp a website’s IP address so as to navigate to that. Then, the name Service (DNS) came on, that interprets numbers into names. therefore after you sort in “www.google.com,” the DNS interprets that back to 8.8.8.8. this permits North American nation to navigate the net rather more handily, as it’s a lot of easier to recall a website’s name than its IP address.
The common variety of IP address (is referred to as IPv4, for "version 4").
Here's example of what IPv4 look like:
66.171.248.170
An IPv4 address consists of 4 numbers, every of that contains one to a few digits, with one dot (.) separating every range or set of digits. every of the four numbers will vary from zero to 255.
Have we run out of IPv4 addresses?
IPv4 contains a theoretical limit of 4.3 billion addresses, and in 1980, that was over enough. however because the net grew and went world, we have a tendency to quickly ran out of addresses, particularly in today’s era of smartphones and IoT devices.
The internet has been running out of IPv4 addresses since the Nineties. whereas clever engineers have found ways that round the drawback, it wasn’t long before a additional permanent fix became the goal. Developed to resolve these capability problems permanently, IPv6 was required once IPv4 may not support the load.
At present, IPv4 coexists on the web with its newer version, although eventually, everything can use IPv6. substitution previous IPv4 instrumentation would be prohibitively pricy and tumultuous, so IPv6 is being slowly extended as older IPv4 hardware is retired.
The IPv6 Address
Internet Protocol version vi, or IPv6, was first introduced at intervals the late Nineteen Nineties as a replacement for IPv4. Even then the builders of world wide web complete IPv4’s limitations and additionally the final word shortage.
IPv6 uses 128-bit addresses, 340,282,366,920,938,463,463,374,607,431,768,211,456, or 340 undecillion addresses. IPv6 addresses ar represented as eight groups of four point illustration system digits, with the groups being separated by colons.
Here example of IPv6 look like is
“7502:0fg6:1201:0142:0110:dh2e:1270:6234,”
but methods to abbreviate this full notation exist.
In addition to increasing the availability of informatics addresses, IPv6 conjointly self-addressed IPv4’s several shortcomings chief among them being security, that we’ll dig into a lot of later.
IPv4/IPv6
Differences
|
IPv4
|
IPv6
|
Address
|
32 bits (4 bytes)
12:34:56:78
|
128 bits (16 bytes)
1234:5678:9abc:def0:
1234:5678:9abc:def0
|
Packet size
|
576 bytes required, fragmentation optional
|
1280 bytes required without fragmentation
|
Packet fragmentation
|
Routers and sending hosts
|
Sending hosts only
|
Packet header
|
Does not identify packet flow for QoS handling
|
Contains Flow Label field that specifies packet flow for
QoS handling
|
Includes a checksum
|
Does not include a checksum
|
Includes options
up to 40 bytes
|
Extension headers used for optional data
|
DNS records
|
Address (A) records,
maps host names
|
Address (AAAA) records,
maps host names
|
Pointer (PTR) records,
IN-ADDR.ARPA DNS domain
|
Pointer (PTR) records,
IP6.ARPA DNS domain
|
Address configuration
|
Manual or via DHCP
|
Stateless address autoconfiguration (SLAAC) using
Internet Control Message Protocol version 6 (ICMPv6) or DHCPv6
|
IP to MAC resolution
|
broadcast ARP
|
Multicast Neighbor Solicitation
|
Local subnet group management
|
Internet Group Management Protocol (IGMP)
|
Multicast Listener Discovery (MLD)
|
Broadcast
|
Yes
|
No
|
Multicast
|
Yes
|
Yes
|
IPSec
|
optional, external
|
required
|
If you like to keep track of these technologies, simply follow me
on Facebook, Twitter, and, or head to my website for
many more in depth articles on these topics. Read other Articles.














No comments:
Post a Comment